BARIUM ENEMA OVERVIEW INDICATION, CONTRAINDICATIONS, SYMPTOMS AND ITS PURPOSE
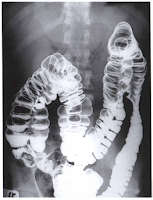 Barium Enema is a radiographic examination of abdomen particularly the large column, x-ray is used to record image on the radiographic film, a combination of contrast media a negative and positive contras media inserted via catheter to make large intestine / bowel visible radiographically. Radiologic technologist usually use the term "barium enema". Furthermore, Barium Sulfate (Positive Contrast Agents) appears white on radiograph as xray are absorbed by this medium. Air, Oxygen, Gas, Nitrogen, Carbon Dioxide is also use as a negative contrast to add black shades on large intestine, this combination makes large bowel and its inside segments creates an clear and optimal images of the large bowel. Other name for barium enema is BaE and lower Gastrointestinal Series or Large intestine x-ray.
Barium Enema is a radiographic examination of abdomen particularly the large column, x-ray is used to record image on the radiographic film, a combination of contrast media a negative and positive contras media inserted via catheter to make large intestine / bowel visible radiographically. Radiologic technologist usually use the term "barium enema". Furthermore, Barium Sulfate (Positive Contrast Agents) appears white on radiograph as xray are absorbed by this medium. Air, Oxygen, Gas, Nitrogen, Carbon Dioxide is also use as a negative contrast to add black shades on large intestine, this combination makes large bowel and its inside segments creates an clear and optimal images of the large bowel. Other name for barium enema is BaE and lower Gastrointestinal Series or Large intestine x-ray.Large Intestine Double Contrast
Purpose of Barium Enema is to study the form, physiological property of large intestine, and detection of abnormal conditons and function of the large intestine. Single contrast and double contrast barium enema are both required to study the entire large bowel for an accurate diagnosis.Contraindication of Barium Enema
Large Bowel Obstruction and a possible hollow viscus patients should not be given barium as a contrast agent. These two contraindication are the same to the small bowel series indications against the advisability. Water soluble contrast media can be used for the patient have these conditions. In spite of the fact that water soluble contrast media are not as radiopaque as barium sulfate.Radiologic Technician must carefully review the patient charts and clinical history to prevent problems during the procedure and radiologist should be informed of any condition noted in the patient chart so that radiologist will know if what study to perform on patient regarding to its condition.
 Previous sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy study or a biopsy of the colon also must be reviewed on patient charts before proceeding into barium enema because performing the procedure will make the involved portion of the colon wall may be weakened and may lead to perforation during the study of barium enema and before initiating the procedure the radiologist must be informed about the patient condition.
Previous sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy study or a biopsy of the colon also must be reviewed on patient charts before proceeding into barium enema because performing the procedure will make the involved portion of the colon wall may be weakened and may lead to perforation during the study of barium enema and before initiating the procedure the radiologist must be informed about the patient condition.Appendicitis is one condition that generally barium enema is contraindicated or is not to be performed because of the risk of perforation or a raptured portion of the large intestine. Ultrasound with High resolution graded compression and computed tomography is now the technique used by other modern hospitals for the condition and diagnosis of acute appendicitis if the clinical indication are not clear.
Large Intestine Single Contrast Study
Pathologic Indication and Symptoms that usually Barium Enema Study will be performed.
Colitis - It is an inflamtion of the large intestine or colon either the colon, cecum or rectum are inflamed. It is also known as Crohn's Disease if diagnosis is unkwnon. An acute or self limited or chronic is termed as Colitides if it is continuing to develop and widely spread is applicable on the category of digestive diseases.Ulcerative Colitis - it cause is unknown it also an inflammation of the large intestine. Usual symptoms of Ulcerative colitis are rectal bleeding, abdominal pain and diarrhea. Barium enema is performed to diagnose ulcerative colitis but sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy is most accurate and with direct visualization means if diagnosis. Ulcerative colitis extending over a long time is a risk factor for a colonic cancer. It can also cause an inflamation in liver including its bile ducts, spine, skin, and joint.
 Diverticulum - is a small out-pouching in the out side wall of large intestine. One or more diverticulum termed as diverticula. The rectum is the common section of large intestine that the diverticulum develops where intestinal material are in final process (feces, stools) that are changing to an greater degree in becoming solid. Diverticula is common in old ages with developed many diverticula. There is a type of congenital diverticulum the Meckel's Diverticulum is pouch on the lower part of intestinal wall that is present since the baby is born and may contain tissue of stomach or pancreatic tissue cells. There three types of Diverticular Diseases.
Diverticulum - is a small out-pouching in the out side wall of large intestine. One or more diverticulum termed as diverticula. The rectum is the common section of large intestine that the diverticulum develops where intestinal material are in final process (feces, stools) that are changing to an greater degree in becoming solid. Diverticula is common in old ages with developed many diverticula. There is a type of congenital diverticulum the Meckel's Diverticulum is pouch on the lower part of intestinal wall that is present since the baby is born and may contain tissue of stomach or pancreatic tissue cells. There three types of Diverticular Diseases. Intussusception - is the sliding of one portion or section of the large intestine and it is termed as telescoping because its like a telescope that slides and folds to together and become shorter its length, when it happens to the intestine results in obstruction that blocks the bowel in a way of compressing against each other. Majority of this pathologic condition is in children but the cause are unknown. In some case the cause of intussusception in children is the Meckel's Diverticulum because of the pouch in the intestinal wall. Barium enema study is not only diagnostic but it may also be therapeutic because air contrast media are inflated and liquids barium enema is injected this will bloats the intestine and have a possibility of disengaging the slidden part of the intestine
Neoplasm - is an abnormal proliferation / devepment of cell which result in the formation of abnormal mass of tissue. Neoplasm develops in the large intestine are common. However benign tumor in the large intestine do occur, most of the carcinoma of the large intesting occurs in the rectum and sigmoid part of the large intestine (colon). "Apple-core" and "napkin-ring"lessions are use as descriptive terms of radiographic appearance and demonstrated during barium enema. Polyps is the onset for both benign and malignant tumors.
Annular Carcinoma or Adenocarcinoma - is the most common characteristic form of colon cancer, and may appear as an Apple core or napkin ring as it grows and penetrates the tissue spaces of the bowel or large intestinal wall and results generally in a large intestine obstructions.
Polyps - this is similar to diverticula but polyps project inwards into the lumen of colon rather than outward. Polyps can be inflamed and become a source of bleeding just like diverticula and for that reason it polyps may have to remove surgically. The most capable modalities used to demonstrate colinic neoplasm are the Barium enema, CT scan and Computed Tomography colonography.
Volvulus - It is twisting of a portion of the large intestine on its own peritoneal membrane and causing to a mechanical obstruction. It may be found in the protion of the jejunum, illeum and or cecum. The twisted portion of the colon causing blood suuply to suspend its flow on this portion and results in obstruction and necrosis. When performing barium enema the usual sign called "beak" sign, a narrowing to one end at the volvulus site will be demonstrated and it will produce an air-fluid level and it is well demonstrated in an erect abdomen projection.
Cecal volvulus - is being a sing of the ascending colon and cecum as having a long mesentery which make them more capable of forming a volvulus.
PATIENT PREPARATION LAXATIVES
Preparation of the patient for a barium enema is more involved than is preparation for the stomach and small bowel. The final objective, however, is the same.The section of alimentary canal to be examined must be empty.
Thorough cleansing of the entire large bowel is of paramount importance for a satisfactory contrast media study of the intestine.
CONTRAINDICATION TO LAXATIVES
Certain conditions contraindicate the use of very effective cathartics or purgative needed to thoroughly cleanse the large bowel. These exemptions includes 1. gross bleeding 2. severe diarrhea 3. obstruction and 4. inflamatory conditions such as appendicitis.BARIUM ENEMA RADIOGRAPHIC ROOM PREPARATION
The radiographic room should be prepared in advance of the patient'' arrival. The fluoroscopy room and the examination table should be clean and tidy for each patient. The control panel should be set for fluoroscopy, with the appropriate technical factors selected. The fluoroscopy timer may be set up to its maximum time, which is usually 5 minutes. If conventional fluoroscopy is used, the photo-spot mechanism should be in proper working order and a supply of spot fiim cassettes handy. The appropriate number of conventional cassettes of appropriate size should be provided for the radiologist, as should lead aprons for all other personel present in the room. The fluoroscopic table should be place in the horizontal position, with water proof backings or disposable pads place on the tabletop. Water proof protection is essential in case of premature evacuation of the enema. The bucky tray must be positioned at the floor end of the table if the fluoroscopy tube is located beneath the tabletop. This will expand the bucky slot shield, reducing gonadal dose to the fluoroscopist. The radiation foot control switch should be place appropriately for the radiologist or the remote control area prepared. Tissue, towels, replacement linens, bed pan, extra gown, a room air freshener, and waste receptacle should be readily available. The appropriate contrast medium or media, container, tubing, and enematip should be prepared. A proper lubricant should be provided for the enema tip. The type of barium sulfate used and the concentration of the mixture vary considerably, depending on radiogist preferences and the type of examination to be performed.BARIUM ENEMA EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES
Barium Enema Containers
 |
| Close System Barium Enema Container |
This system, which is shown in the photograph, includes the disposable enema bag with pre measured amount of barium sulfate. Once mixed, the suspension travels down its own connective tubing and flow is controlled by a plastic stopcock. An enema tip is placed on the tubing and is inserted into the patient''s rectum.
After the examination has been completed, much of the barium can be drained back into the bag by lowering the system to below table top level. The entire bag and tubing are disposed of after a single use.
ENEMA TIP
Various type and sizes of enema tips are available. The three most commone are:Plastic Disposable
Rectal Retention
Air Contrast retention enema tips.
Rectal Disposable Retention Tips
Is sometimes called retention catheters, are used on those patients who have relaxed anal sphinchers of those who cannot for any reason retain the enema. These rectal retention catheters consist of double lumen tube with a thin rubber balloon at the distal end. After rectal insertion, this balloon is inflated carfully with air through a small tube to assist the patient in retaining the barium enema. These rentention catheter should be fully inflated only under fluoroscopic guidance provided by the radiologist because of the potential danger of intestinal rapture. To prevent discomfort for the patient, the balloon should not fully inflated until the fluoroscopy procedure begins.A special type air contrast retention enema tips is needed to inject air through a separate tube into the colon, where it mixes barium for double contrast BE exam. These are all considered single use, disposable enema tips.
LATEX ALLEGIES
Today, most products are primary latex-free, but determination of whether the patient is sensitive to natural latex latex products is still important. Patients with sensitive towards latex experience anaphylactoid type reaction that include sneezing, redness, rash, difficulty in breathing and even death.If the patient has a history of latex sensitivity, the technologist must ensure that the enema tip, tubing, and gloves are latex free. Even the dust produced by removal of gloves may introduce into the air latex protein, which may be inhaled by the patient. Technologist with sensitivity must be keenly aware of the type of gloves, catheters, and other latex devices found in the department. If rash develops while the technologist is wearing gloves or handling certain objects, he or she should consult a physician to explore the possibility of latex sensitivity.
CONTRAST MEDIA
Barium sulfate is the most common type of positive contrast medium used for the barium enema. The concentration of the barium sulfate suspension varies according to the study performed.A standard mixture used for single contrast media barium enemas ranges between 15% to 25% weigth to volume (w/v).
The thicker barium sulfate solution introuduced during a CT scan of the large intestine processes a low w/v to prevent artifacts from being produced that may obscure anatomy. The evacutive proctogram requires a contrast media with a minimum weigth to volume of 100%
NEGATIVE CONTRAST AGENTS
The double contrast media uses a number of negative contrast agents, in addition to barium sulfate. Room air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide are the most common form of negative contrast media used. Carbon dioxide is gaining wide use because it is well tolerated by the large intestine and is absorb rapidly after the procedure. Carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas are stored in a small tank and can be introduced into the rectum. An iodinated, water-soluble contrast media may be used in a case of a perforated or located intestinal wall, or when the patient is scheduled for surgery after the barium enema.Remember that a medium range kV (80 to 90) should be used with a water soluble, negetive-contrast agent. Usually patients who are scheduled for Barium Enema are instructed to NPO or atleast 6-8 hrs. Take laxatives after dinner to cleanse inside the large bowel. At night Fruits and Fresh Juices are the best food and drinks to take before the barium enema procedure.