Head Scan MRI
Brain MRI are usually done with the patient supine on the
examination couch with their head within the head coil. The head is adjusted so
that the interpupillary line is parallel to the couch and the head is straight.
The longitudinal alignment light lies in the midline of the patient, while
horizontal alignment light passes through the nasion. Straps and foam pads are
used for immobilization. Brain MRI is done to diagnose these common indication:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Primary tumour assessment and or metastatic disease.
- AIDS (toxoplasmosis)
- Infarction – cerebral vasvular accident (CVA) vs Transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
- Haemorrhage
- Hearing Loss
- Visual disturbances
- Infection
- Trauma
- Unexplained neurological symptoms or deficit
- Pre-operative Planning
- Radiation Treatment Planning
- A Follow-up after surgical or treatment
Equipment Needed when performing Brain MRI:
- Head Coil (quadrant or multi-coil array)
- Immobilization pads and straps
- Ear plugs
- High performance gradients for EPI, diffusion and perfusion imaging
Suggested Protocol Head / Scan MRI
 |
|
Sagittal SE T1 weighted midline slice
of the brain showing
the axis of the
anterior and posterior commissures
|
Sagital SE / FSE Incoherent (spoiled) GRE T1
The medium slices or gap are prescribed on each of the
longitudinal alignment light from one temporal lobe to the other. The area from
the foramen magnum to the top of the head is included in the image. Left is 37
mm to Right 37 mm.
Axial or Oblique SE / FSE PD / T2
Medium slices or gap are prescribed from the foramen magnum
to the superior surface of the brain. Slices may be angled so that they are
parallel to the anterior and posterior commissure axis. This enables precise
localization of lessions from reference to anatomy atlases. Many sites have
replaced the PD sequence with FLAIR. SS-FSE or SS-EPI may be a necessary
alternative for a rapid examination in uncooperative patients.
Coronal SE / FSE PD / T2
As for axial PD / T2, except prescribe slices from the
cerebellum to the frontal lobe.
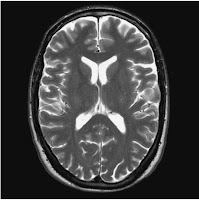 |
| Axial/oblique FSE T2 weighted image of the brain showing normal appearances |
Additional Sequences MRI Head Scanning
Axial or Oblique IR T1
Slice prescription as for Axial / oblique T2
This sequence is very useful in imaging of the pediatric
brain. White matter does not fully myelinate until approximately 5 years of
age, therefore in the very young patient, grey and white matter have very
similar T1 relaxation times, and the CNR between these tissues is small on SE
T1 sequences.
Axial or Oblique FLAIR / EPI
This sequence provide a quick acquisition with stoppage of
CSF signal. It very useful in studying periventricular or cord lesions like MS
plaques. Periventricular abnormalities will have a high signal intensity in contrast to the low signal of CSF which has been nulled using a long TI as shown in the image of Axial or Oblique FLAIR brain scan.
 |
| Axial/oblique incoherent (spoiled) GRE image of the brain. |
Axial / Oblique SE / FSE Incoherent (spoiled) GRE T1
 |
| SS-FSE T2 weighted image of the brain. |
SS – FSE T2 Brain Scan
A brain scan MRI and very useful for rapid imaging if the patient in uncooperative. In the image shows a weighted image of the brain. MRI scan of entire brain with SS – FSE T2.Axial 3D incoherent (spoiled) GRE T1 Brain Scan
It is a high resolution
imaging sequence and useful for imaging of small structures in the brain. An
isotropic dataset must be acquired when reformatting of desired slices.
Axail Oblique GRE / EPI T1 and T2
If demonstration of hemorrhage
is it better than SE and FSE. Due to sensitivity of magnetic susceptibilities.








No comments:
Post a Comment